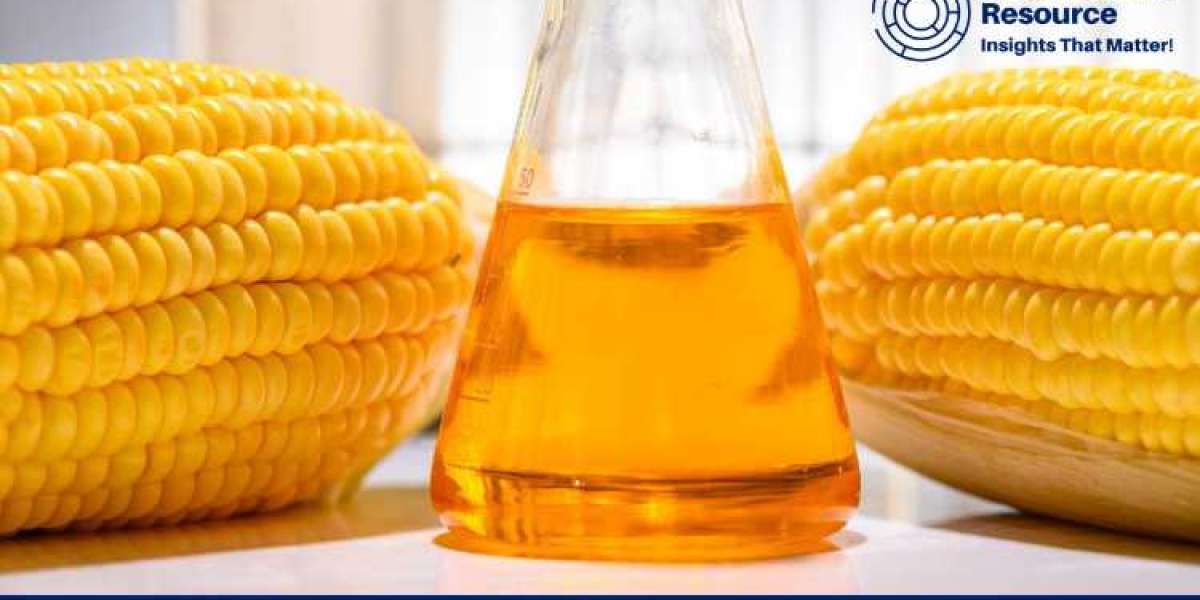
Corn, as one of the world’s most widely cultivated crops, plays a central role in global agriculture. Its pricing affects not only farmers and traders but also industries like animal feed production, biofuels, and food manufacturing. Understanding corn price trend involves examining historical data, identifying market drivers, and considering future projections. This analysis provides a comprehensive look at the factors influencing corn prices, the historical patterns, and the insights needed for informed decision-making.
Historical Corn Price Patterns
Corn prices have historically been influenced by a combination of supply-and-demand dynamics, weather patterns, policy decisions, and broader economic conditions. Some notable trends include:
- Seasonal Fluctuations:
- Corn prices often follow a predictable seasonal pattern, peaking before harvest when supply is uncertain and dropping after harvest when supplies increase.
- This cycle repeats yearly, though external factors can disrupt the pattern.
- Long-Term Price Cycles:
- Over the decades, corn prices have experienced boom-and-bust cycles tied to technological advances, changes in farming practices, and shifts in global demand.
- Periods of high prices are often followed by increased planting and eventual oversupply, which can drive prices down.
- Economic and Policy Impacts:
- Major policy shifts, such as the U.S. ethanol mandate, have historically pushed corn prices higher.
- Global financial crises, trade agreements, and tariffs have also contributed to price volatility.
Enquire For Regular Prices: https://www.procurementresource.com/resource-center/corn-price-trends/pricerequest
Key Drivers of Corn Price Trends
Several factors consistently shape the trajectory of corn prices on both short- and long-term scales:
Supply-Side Factors:
- Weather and Climate:
- Adverse weather conditions, such as droughts, floods, or unseasonal frosts, can reduce yields and drive prices upward.
- Longer-term climate patterns and shifting growing zones also play a role in overall production levels.
- Production Costs:
- Rising costs for inputs like fertilizer, seeds, and fuel can lead to higher break-even prices for farmers, indirectly influencing market prices.
- Technological Advancements:
- Innovations in seed technology, irrigation methods, and precision agriculture tend to boost yields and increase supply, putting downward pressure on prices.
- Global Crop Competition:
- The price and availability of alternative feed grains (such as wheat and barley) can affect corn prices. When other crops are abundant, demand for corn may soften, leading to lower prices.
- Weather and Climate:
Demand-Side Factors:
- Animal Feed:
- Livestock and poultry production are key drivers of corn demand. Growth in meat consumption, particularly in developing countries, directly impacts corn prices.
- Biofuels and Ethanol Production:
- Corn is a major feedstock for ethanol production. Policy changes, crude oil price fluctuations, and the growth of renewable energy sources can all influence ethanol demand and, consequently, corn prices.
- Export Markets:
- Global trade flows, currency exchange rates, and economic growth in importing countries affect international demand for U.S. corn.
- Major buyers such as China and Mexico have a significant impact on price levels.
- Consumer Preferences and Food Production:
- Corn’s role as a staple ingredient in processed foods, sweeteners, and beverages ensures steady demand. Changes in dietary trends or consumer preferences can subtly influence overall demand.
- Animal Feed:
Macroeconomic and Geopolitical Influences:
- Currency Exchange Rates:
- The strength of the U.S. dollar can impact the competitiveness of U.S. corn exports. A strong dollar often makes U.S. corn more expensive for international buyers, potentially reducing demand.
- Trade Policies and Tariffs:
- Trade agreements, sanctions, and tariffs can disrupt traditional trade routes, causing price fluctuations.
- Global Economic Conditions:
- Economic slowdowns or recessions can reduce demand for feed and ethanol, putting downward pressure on prices. Conversely, periods of economic growth often increase demand and support higher prices.
- Currency Exchange Rates:
Regional Insights and Analysis
Corn price trends vary across regions, influenced by local growing conditions, domestic policies, and proximity to major markets:
- United States:
- As the largest corn producer and exporter, U.S. prices heavily influence global benchmarks.
- The Midwest Corn Belt dominates production, with weather conditions in these states often setting the tone for annual price movements.
- South America:
- Brazil and Argentina are major exporters, and their harvest cycles complement those in the Northern Hemisphere.
- Currency devaluations and weather patterns (such as La Niña or El Niño) in South America can have significant ripple effects on global corn prices.
- China:
- As one of the largest corn consumers, China’s domestic production, stockpiling policies, and import decisions greatly influence international prices.
- Any shortfall in Chinese production or a sudden increase in imports can cause global prices to spike.
- Europe and the Black Sea Region:
- The Black Sea region, including Ukraine and Russia, has become an important source of corn exports.
- Political instability, trade restrictions, and weather conditions in this region can cause price volatility on the global stage.
Future Outlook and Forecasts
While no prediction is certain, certain trends and factors provide insight into how corn prices may evolve:
- Emerging Markets and Population Growth:
- Continued population growth and rising incomes in developing countries are expected to increase demand for meat, feed grains, and processed foods, supporting long-term price stability.
- Climate Change and Crop Adaptation:
- Changes in growing conditions may cause shifts in production areas and yield potential, introducing both risks and opportunities for price trends.
- Farmers adopting resilient seed varieties and innovative practices could mitigate some of the upward pressure caused by climate-related disruptions.
- Biofuel Policy Changes:
- The push for renewable energy and potential changes to biofuel mandates could significantly alter corn demand.
- Advancements in cellulosic ethanol or alternative biofuels might reduce reliance on corn, potentially tempering price growth.
- Technological Breakthroughs:
- Continued investment in agricultural technology, including genetic editing, precision farming, and data-driven crop management, is likely to improve yields and contain costs.
- Over time, these advances may lead to more stable prices by reducing the impact of supply shocks.
- Geopolitical and Trade Dynamics:
- Ongoing trade negotiations, new free trade agreements, or geopolitical conflicts can shift trade patterns and affect global supply chains, influencing future price trends.
Corn price trends reflect a complex web of supply-and-demand dynamics, weather conditions, technological innovations, and geopolitical factors. By analyzing historical patterns, market drivers, and regional influences, stakeholders can gain a clearer understanding of how corn prices evolve over time. This information is critical for making strategic decisions, managing risk, and seizing opportunities in the global agricultural market.
Contact Us:
Company Name: Procurement Resource
Contact Person: Leo Frank
Email: sales@procurementresource.com
Toll-Free Numbers:
- USA Canada: +1 307 363 1045
- UK: +44 7537171117
- Asia-Pacific (APAC): +91 1203185500
Address: 30 North Gould Street, Sheridan, WY 82801, USA