When it comes to viral infections, two terms that often cause confusion are Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex. While both belong to the herpesvirus family, they represent different conditions with unique characteristics. Understanding the differences between Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex can help you recognize symptoms, seek appropriate treatment, and take preventive measures. In this article, we’ll break down the key distinctions.
What Are They?
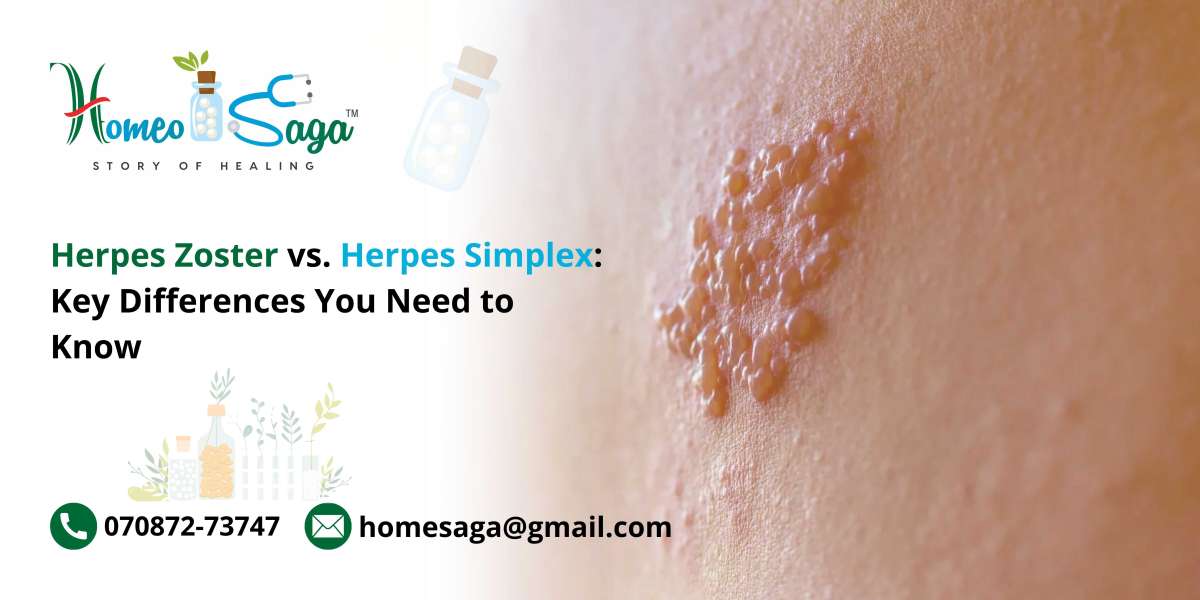
Herpes Zoster, more commonly known as shingles, is caused by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV). This is the same virus that causes chickenpox. After an individual has chickenpox, the virus remains dormant in the body, residing in nerve cells. It can reactivate later, often due to stress, illness, or a weakened immune system, leading to shingles.
Herpes Simplex, on the other hand, refers primarily to two types of viruses: Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 is typically associated with oral herpes, leading to cold sores, while HSV-2 is primarily linked to genital herpes. Both types are highly contagious and transmitted through direct contact with an infected person.
Recognizing Symptoms
Identifying the symptoms of these infections is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
- Initial Pain: Often, shingles begins with localized pain, tingling, or burning in a specific area, which may occur a few days before any visible rash.
- Rash Appearance: A rash typically appears as clusters of red blisters, which eventually fill with fluid and then crust over. This rash usually follows a dermatomal pattern, affecting one side of the body.
- Associated Symptoms: Patients may experience fever, fatigue, and sensitivity to light.
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex
- HSV-1 Symptoms: Cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth are the hallmark of HSV-1. Before the sores develop, individuals may feel itching or a tingling sensation.
- HSV-2 Symptoms: This type results in painful blisters in the genital area, often accompanied by itching and flu-like symptoms during initial outbreaks.
Transmission Methods
The ways these viruses spread are significantly different.
Herpes Zoster Transmission
Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex is not directly contagious. However, someone who has never had chickenpox can contract the virus from someone with shingles by coming into contact with the fluid from the blisters, leading to chickenpox, not shingles.
Herpes Simplex Transmission
Herpes Simplex is highly contagious and can be easily spread through skin-to-skin contact. This includes kissing, sexual contact, and even sharing utensils or towels with an infected person.
Treatment Options
Each condition has specific treatment protocols.
Treatment for Herpes Zoster
The mainstay of treatment for Herpes Zoster includes antiviral medications such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir. Early intervention with these medications can reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Pain management is also essential, often requiring over-the-counter pain relievers or stronger prescription medications for severe cases.
Treatment for Herpes Simplex
For Herpes Simplex, antiviral treatments like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are effective in managing outbreaks and decreasing the frequency of recurrences. Topical treatments may also help alleviate discomfort associated with cold sores.
Preventive Strategies
Preventing these infections involves different approaches.
Preventing Herpes Zoster
A vaccine is available to reduce the risk of developing Herpes Zoster, especially recommended for adults over 50. The shingles vaccine can significantly decrease the likelihood of outbreaks and related complications.
Preventing Herpes Simplex
To prevent Herpes Simplex, it's essential to avoid direct contact with sores. Using barrier methods during sexual activity and practicing good hygiene can help reduce the risk of transmission.
Conclusion
In conclusion, while Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex may share a similar name, they are distinct conditions with unique symptoms, causes, and treatment options. Understanding the differences between Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex is vital for effective management and prevention. If you suspect you have either condition, it’s important to consult a healthcare professional for a proper diagnosis and treatment plan. Armed with the right knowledge, you can take proactive steps to manage your health and well-being.