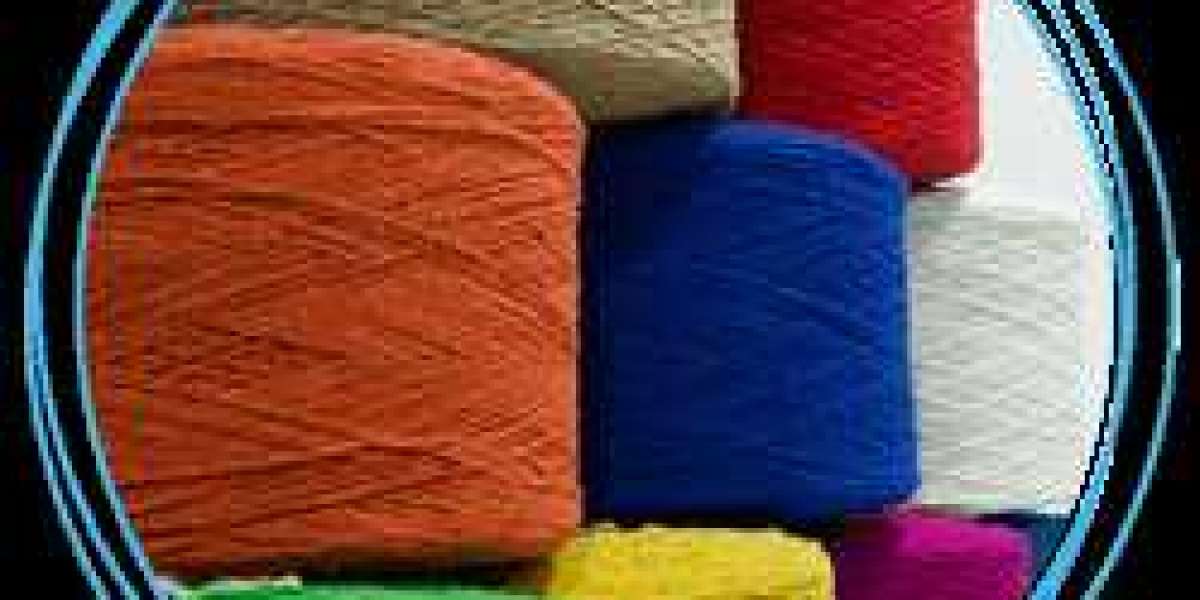
As sustainability becomes a key priority across industries, the textile sector is no exception. Recycled yarn is transforming the way manufacturers approach fabric production, reducing environmental impact while meeting the demands of eco-conscious consumers. India is at the forefront of this sustainable shift, thanks to its strong textile foundation and technological advancements. This blog will highlight the importance of recycled yarn, why India leads in this space, and how manufacturers like Jindal Textile are contributing to a greener future.
Understanding Recycled Yarn:
Recycled yarn is created by processing waste materials, such as used fabrics, plastic bottles, and other synthetic and natural fibers, into new yarn. This innovative process offers significant environmental benefits, including:
- Reduces Waste: Diverts textile and plastic waste from landfills and reduces the burden on waste management systems.
- Lower Energy Use: Consumes less energy compared to the energy-intensive process of producing virgin yarn from raw materials.
- Minimizes Water Usage: Significantly reduces water consumption, a critical factor in regions facing water scarcity, compared to conventional yarn manufacturing that often uses vast amounts of water.
- Decreases Greenhouse Gas Emissions: Helps reduce the carbon footprint of textile production by curbing emissions generated during raw material processing.
The Recycled Yarn Production Process:
To understand the benefits fully, it’s essential to appreciate how recycled yarn is produced:
- Collection of Waste Materials: This involves sourcing textile waste, post-consumer garments, and plastic bottles.
- Sorting and Cleaning: The waste materials are sorted based on color and type to minimize the need for additional dyeing, which can be water-intensive.
- Shredding and Fiber Extraction: The sorted waste is broken down into smaller pieces and processed to extract fibers.
- Spinning: The extracted fibers are spun into new yarn, which can be used to produce fabrics for clothing, home textiles, and more.
- Quality Control: Ensuring the yarn meets industry standards for strength, consistency, and durability is a crucial final step.
India’s Leadership in Recycled Yarn Production:
India’s leadership in recycled yarn manufacturing is due to a combination of historical expertise and modern innovation. Several factors contribute to the country’s prominence:
- Established Textile Infrastructure: India’s rich textile heritage has laid a robust foundation for the transition to sustainable practices. Decades of experience have enabled manufacturers to adapt and innovate seamlessly.
- Government Support: Policies and incentives from the Indian government encourage sustainable practices. Initiatives like the ‘Make in India’ campaign and sustainable development programs focus on promoting eco-friendly manufacturing.
- Technological Advancements: The Indian textile industry has adopted modern machinery and technology that facilitate efficient recycling processes. Innovations in fiber extraction and mechanical recycling have improved the quality and strength of recycled yarn.
- Growing Awareness: Increased awareness about sustainability among Indian consumers and businesses has fueled demand for eco-friendly products, pushing manufacturers to integrate greener practices.
Challenges in Recycled Yarn Production:
While recycled yarn production offers numerous benefits, it does come with its challenges:
- Quality Consistency: Achieving consistent quality can be complex, as recycled materials often vary in composition.
- Higher Initial Costs: Implementing recycling technology and setting up facilities require significant initial investment, although long-term savings and environmental benefits often offset these costs.
- Color Matching and Dyeing: Working with pre-colored waste materials can limit the dyeing flexibility, requiring innovative solutions for color uniformity without excessive water use.
- Supply Chain Management: Securing a steady supply of post-consumer and post-industrial waste poses logistical challenges, especially in maintaining quality standards.
Benefits of Using Recycled Yarn:
Businesses choosing recycled yarn can reap several advantages, enhancing both their operational and brand value:
- Sustainability Credentials: Incorporating recycled yarn into products demonstrates a company’s commitment to eco-friendly practices, resonating with environmentally aware consumers who prioritize sustainability.
- Cost Savings: While the initial setup for recycled yarn production can be high, streamlined processes and bulk recycling can lead to cost savings over time.
- Versatile Applications: Recycled yarn can be used for a wide range of products, including apparel, home textiles, upholstery, and even technical fabrics. This flexibility allows brands to offer sustainable options across different product categories.
- Reduced Dependence on Virgin Materials: By incorporating recycled yarn, manufacturers reduce reliance on virgin resources, such as raw cotton or new synthetic fibers, thereby contributing to the conservation of natural resources.
Jindal Textile’s Role in Recycled Yarn Manufacturing:
Jindal Textile exemplifies industry leadership through its dedication to sustainable practices. As an advocate for eco-friendly production, Jindal integrates several key principles:
- High-Quality Materials: The company sources post-consumer and post-industrial waste to produce yarn that meets high-quality standards, ensuring durability and aesthetic appeal.
- Advanced Recycling Techniques: Jindal Textile uses state-of-the-art machinery and processes that minimize energy consumption and optimize output, supporting both environmental and economic sustainability.
- Commitment to Eco-friendly Practices: Every step of Jindal Textile’s recycled yarn production process adheres to strict environmental guidelines, including reduced water usage and lower emissions.
- Partnerships and Collaborations: Collaborating with environmental organizations and research bodies, Jindal Textile stays at the forefront of sustainable innovation and contributes to community-level recycling initiatives.
Future Trends in Recycled Yarn:
The industry’s future points towards more sustainable and innovative practices, with potential trends including:
- Biodegradable Fiber Blends: Combining recycled fibers with biodegradable natural materials could enhance the sustainability quotient of yarn.
- Circular Economy Models: Manufacturers are beginning to implement closed-loop systems where old textiles are collected, recycled, and reintegrated into new production cycles.
- Smart Recycling Technology: The use of AI and IoT in sorting, quality control, and process optimization can make recycling more efficient and cost-effective.
- Expanding Consumer Education: Brands and manufacturers are investing in educational campaigns to inform consumers about the benefits of recycled yarn, promoting wider adoption and increased demand.
Conclusion:
The transition to recycled yarn is an essential step toward achieving sustainability in the textile industry. With its expertise, technological advancements, and commitment to eco-friendly practices, Jindal Textile, recycled yarn manufacturers in India stands out as a trusted partner for businesses looking to embrace greener production methods. By sourcing recycled yarn from established manufacturers like Jindal, companies can align their operations with global sustainability goals and meet the growing consumer expectation for responsible and innovative products. Embracing recycled yarn not only supports environmental efforts but also positions brands to be leaders in the sustainable fashion movement.