Understanding the Evolution of Hearing Aid Technology
As we delve into the world of it, it becomes clear that it has a vast and complex history right invisible hearing aids.Over the years, the healthcare industry has witnessed a remarkable transformation in the field of hearing aids. From bulky, conspicuous devices to sleek and virtually undetectable ones, the evolution of invisible hearing aids has revolutionized the way individuals with hearing loss experience the world around them.
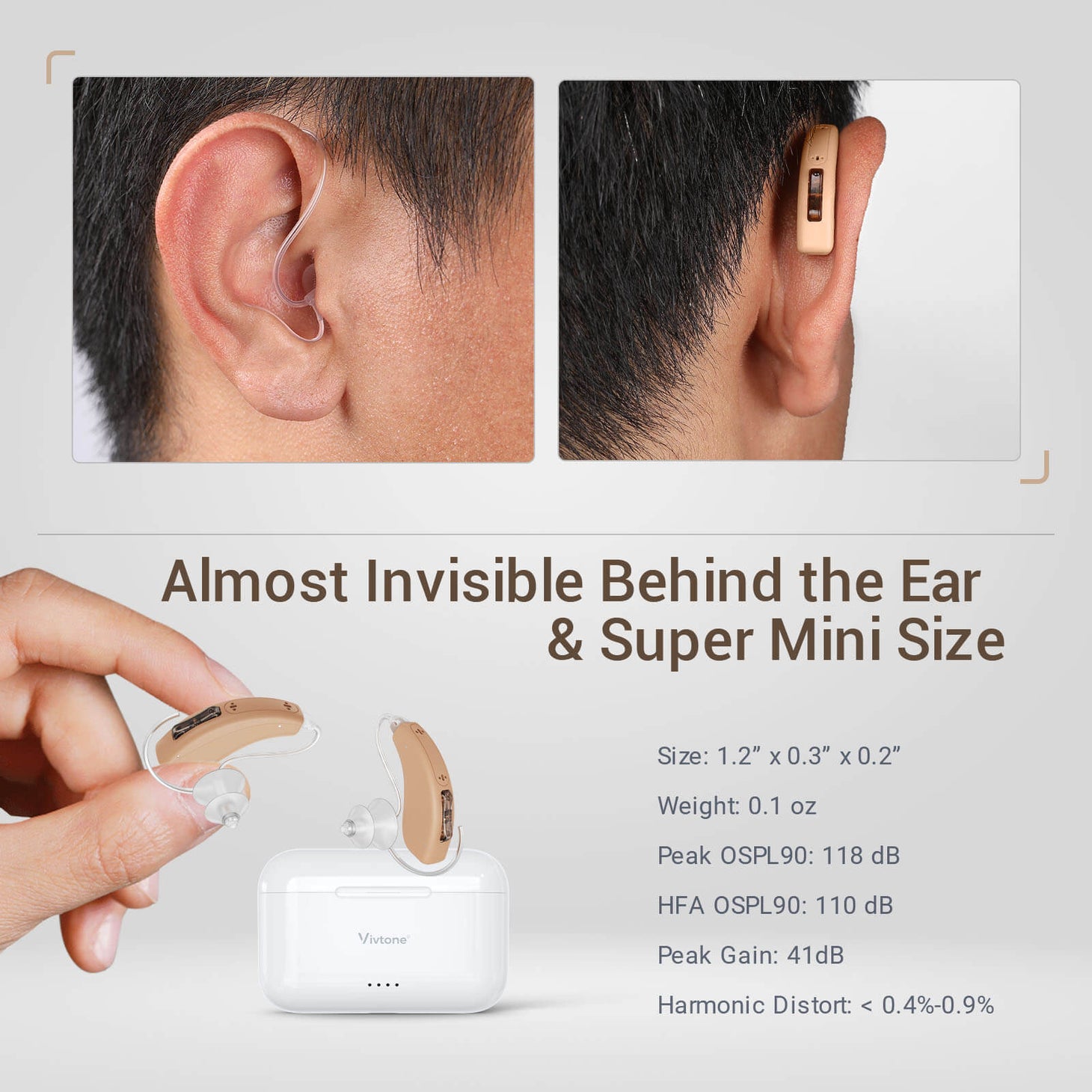
The Advantages of Invisible Hearing Aids
One of the key benefits of invisible hearing aids is their discreet nature. Unlike traditional hearing aids that are easily visible, these innovative devices are designed to sit deep within the ear canal, making them virtually invisible to others. This not only enhances the wearer's confidence but also eliminates the stigma associated with hearing loss.
Technological Innovations Driving the Adoption of Invisible Hearing Aids
The rapid advancement of technology has played a significant role in the rise of invisible hearing aids in the healthcare industry. From miniaturized components to sophisticated algorithms, these devices are now capable of delivering superior sound quality and personalized listening experiences. Additionally, features such as wireless connectivity and smartphone compatibility have made invisible hearing aids more convenient and user-friendly than ever before.
The Future of Hearing Aid Technology
As the demand for invisible hearing aids continues to grow, we can expect to see further innovations in the field of hearing aid technology. From AI-powered devices that adapt to the user's environment to biometric sensors that monitor overall health, the future holds immense potential for enhancing the lives of individuals with hearing loss.







