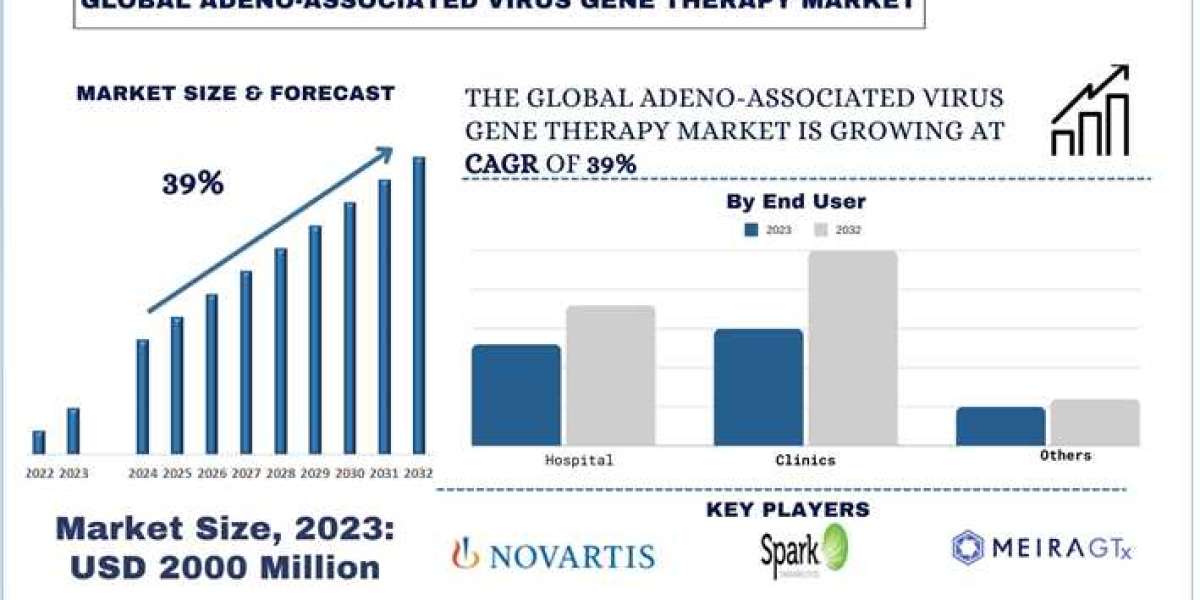
Among all the existing methods of treatment in the sphere of modern medicine, gene therapy is one of the most significant innovations featuring the possibility of changing the therapeutic management paradigm of extensive varieties of genetic ailments. In contrast to most available treatments, gene therapy focuses on the cause of these conditions – mutations in the DNA and aims at altering, replacing, or deleting the mutated genes and, as such, holds tremendous potential of offering treatment to patients diagnosed with hitherto untreatable or terminal illnesses. Over time, more effective therapies are developed and discovered; thus, as more therapies are brought from the research to clinical stages, the prospect of the future of medical practice is brighter.
Understanding Gene Therapy
Genes therapy is the technique that involves the addition, deletion or modification of genes in a human body with the intention of combating diseases. The most frequent approach involves the use of vectors which an sometimes be a virus as in the case of adeno-associated viruses (AAV) gene therapy market to deliver the therapeutic genes to the patient’s cells. These vectors are created in order to avoid any adverse reactions while delivering the desired therapeutic genes to the right cells and tissues, as well as to make sure they work as expected.
There are several types of gene therapy, including:
- Gene Addition: Incorporating a normal gene as form of replacement for the defective gene which is not functioning optimally.
- Gene Editing: Interventions such as gene editing with methods like CRISPR/Cas9 that aims at directly manipulating and correcting the genetic defects.
- Gene Silencing: Inactivating the genes which are capable of causing biologic harm in the body.
- Gene Regulation: Gene therapy, gene silencing or overexpression of genes to create an effect on the body; a form of treatment.
Gene therapy is gaining a lot of attention with many people looking forward to getting treated through this technique in the near future.
History reveals that Gene therapy has held so much potential for addressing numerous genetic diseases. Here are some areas where it is making a significant impact:
Inherited Retinal Diseases: Congenital diseases such as LCA and RP, which cause gradual vision deterioration and blindness, are among the diseases which have been made progress with gene therapy. Clinical trials have been conducted for human application and recently, Luxturna, an AAV-based gene therapy has been approved for LCA and has given the LCA patients, the hope of seeing the world better.
Hemophilia: Hemophilia A and B for example resulting from deficiency of clotting factors have all along been managed through administration of the factor through infusions. With recursive treatments being an arduous task, gene therapy seeks to cure the disease by introducing genes that will produce the required clotting factors.
Spinal Muscular Atrophy (SMA): SMA is a particularly sub-type of neuromuscular diseases which pertains to motor function. Zolgensma, which is delivery of a functional copy of the missing or defective SMN1 gene using a gene therapy approach based on adeno-associated viral vector, has been approved for the treatment of SMA and has been shown to enhance the survival and motor function in children suffering from SMA.
Cancer: Cancer cure through gene treatment or gene modification is in focus, including curing as well as bolstering the impact of other treatment methods. Take, for example, CAR-T cell therapy, which involves altering a patient’s T cells, so that these cells are better able to identify cancer cells and neutralize them.
Rare Genetic Disorders: Highly pathogenic and low incidence genetic diseases like Duchenne muscular dystrophy (DMD) and phenylketonuria (PKU) are some of the genetic disorders that are targeted for gene therapy. Current studies include the basic treatments and clinical trials to develop and seek for the corrective treatments if there none in existence.
Access sample report (including graphs, charts, and figures): https://univdatos.com/get-a-free-sample-form-php/?product_id=61054
Challenges and Considerations
While the potential of gene therapy is vast, there are several challenges that need to be addressed to fully realize its benefits:
- Safety: Ensuring the safety of gene therapy is paramount. While vectors like AAV have been engineered to be safe, there is still a risk of immune reactions or unintended effects on other genes. Ongoing research aims to minimize these risks.
- Efficacy: Achieving consistent and long-lasting therapeutic effects is a key goal. This involves optimizing vector design, delivery methods, and gene expression levels to ensure that the therapy works as intended over the long term.
- Cost: Gene therapies are often expensive, reflecting the complexity of their development and production. Ensuring access to these treatments requires strategies to reduce costs and provide coverage through healthcare systems and insurance.
- Ethical and Regulatory Issues: Gene therapy raises important ethical and regulatory questions, particularly when it comes to germline editing, which can affect future generations. Establishing clear guidelines and oversight is crucial to navigate these issues responsibly.
The Future of Gene Therapy
However, there is a bright future for the development of gene therapies and a heavy potential for their prognosis. New technologies are opening the door to personalized and efficacious treatments: CRISPR/Cas9 and gene therapy are two examples. While elucidating the roles of genes and molecular agents, plans and objectives are set and developed along the line of target identification and approach to treatment strategies.
Further, initial trails of gene therapies have lots of success so the next stages of trials are getting more acceptance and funding. Principal key players of market are the pharmaceutical industries, bio-tech companies and academic organizations are working more closely to fast track the discovery of advanced therapies. The same has been seen with the regulatory agencies seeking to find ways in which to fast-track the development of gene therapy while at the same time taking care to ensure that all the appropriate measures are in place to protect the public from substandard products.
Conclusion
Gene therapy is a revolutionary way of handling genetic defects the provision of which means a cure rather than the control of the symptoms of a genetic disease. With time and as more of the current research studies yield their drugs that get to the patients, society’ is at the dawn of a new age of medicine where indeed, people have curative treatments as they are customized. Gene therapy’s progress may be still considered as a roadmap of one’s development, but its presence in people’s lives is already raising a hope of the future in which genetic diseases will be no longer a determinant of people’ fate.
Contact Us:
UnivDatos Market Insights
Email - contact@univdatos.com
Contact Number - +1 9782263411
Website -www.univdatos.com