When discussing viral infections, the terms Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex often arise, yet many people may not fully understand what sets them apart. Though both belong to the herpesvirus family, they have distinct characteristics and implications for health. In this article, we’ll explore the key differences between Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex, including their symptoms, causes, treatment options, and prevention strategies.
Understanding the Viruses
Herpes Zoster, commonly known as shingles, is triggered by the reactivation of the varicella-zoster virus (VZV), the same virus that causes chickenpox. After recovering from chickenpox, the virus can remain dormant in the body and may reactivate later in life, often when the immune system is weakened.
Herpes Simplex encompasses two primary types: Herpes Simplex Virus type 1 (HSV-1) and type 2 (HSV-2). HSV-1 is primarily associated with oral herpes, leading to cold sores, while HSV-2 is mostly linked to genital herpes. Both types are easily transmitted through direct contact with an infected person.
Symptoms to Identify
Recognizing the symptoms of these infections is crucial for timely diagnosis and treatment.
Symptoms of Herpes Zoster
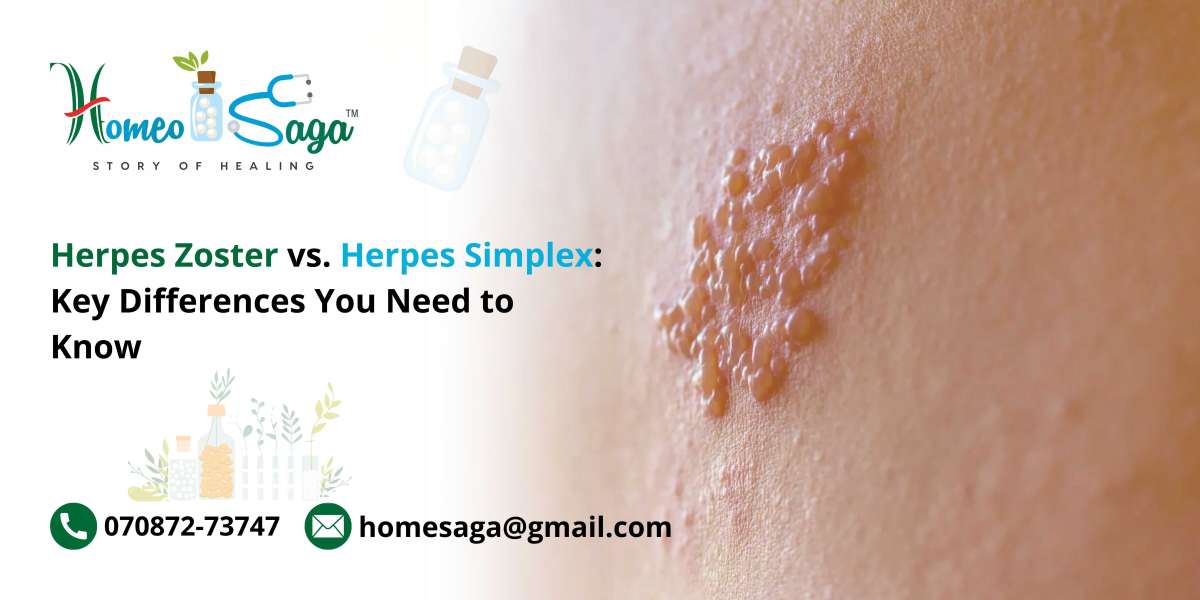
- Localized Pain: The onset often includes a burning or tingling sensation in a specific area, typically occurring days before any rash develops.
- Rash Development: A rash appears, characterized by clusters of red, fluid-filled blisters, usually following a specific nerve pattern on one side of the body.
- Systemic Symptoms: Accompanying symptoms may include fever, fatigue, and sensitivity to light.
Symptoms of Herpes Simplex
- HSV-1 Symptoms: Cold sores or fever blisters around the mouth are common, often preceded by itching or tingling.
- HSV-2 Symptoms: This type results in painful blisters in the genital area, often accompanied by itching and discomfort, especially during the initial outbreak.
How They Spread
Understanding how these viruses are transmitted can aid in prevention.
Herpes Zoster Transmission
Herpes Zoster itself is not contagious in the traditional sense. However, an individual with shingles can transmit the varicella-zoster virus to someone who has never had chickenpox through direct contact with the fluid from the blisters, resulting in chickenpox.
Herpes Simplex Transmission
Herpes Simplex is highly contagious and can be spread through skin-to-skin contact. This includes kissing, sexual activity, and sharing personal items like utensils or towels.
Treatment Options
Both conditions have effective treatment options, but they differ significantly.
Treatment for Herpes Zoster
The treatment for Herpes Zoster typically involves antiviral medications, such as acyclovir, valacyclovir, or famciclovir. These medications are most effective when started early and can help reduce the severity and duration of symptoms. Pain management is also crucial, often requiring over-the-counter pain relievers or prescription medications for more intense pain.
Treatment for Herpes Simplex
For Herpes Simplex, antiviral medications like acyclovir, valacyclovir, and famciclovir are effective in managing outbreaks and minimizing the frequency of recurrences. Topical treatments can provide relief for cold sores.
Preventive Measures
Preventing these infections involves different strategies.
Preventing Herpes Zoster
Vaccination is an effective preventive measure for Herpes Zoster. The shingles vaccine is recommended for adults over 50, significantly reducing the risk of developing shingles and its complications.
Preventing Herpes Simplex
To reduce the risk of Herpes Simplex, avoid direct contact with active sores. Practicing safe sex and good hygiene, such as washing hands frequently and not sharing personal items, can also help prevent transmission.
Conclusion
In summary, while Herpes Zoster and Herpes Simplex are related as members of the herpesvirus family, they are distinct in their symptoms, causes, and treatments. Understanding the differences between Herpes Zoster vs. Herpes Simplex is vital for effective management and prevention. If you suspect you have either condition, seeking medical advice for an accurate diagnosis and treatment plan is essential. By arming yourself with the right information, you can better manage your health and well-being.